Piezoresistive Bistable State Sensor is a microelectomechanical system (MEMS) capable of on-chip sensing of bistable mechanism state using the piezoresistive properties of polysilicon, thus eliminating the need for electrical contacts. Sensing the state of bistable mechanisms is critical for various applications, including high-acceleration sensing arrays and alternative forms of nonvolatile memory.
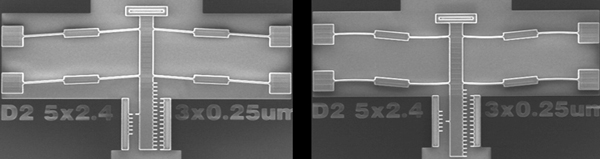
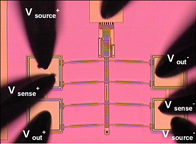
Potential applications for the bistable mechanism with piezoresistive position sensing include mechanical nonvolatile memory and threshold sensing arrays. Bistable mechanisms are well-suited for mechanical nonvolatile memory applications, because they remain in position without any input power. Low-power threshold sensors can also be made such that now power is required during sensing mode and power is only required for interrogation of the sensor. For example, acceleration thresholds can be calculated using an array of mechanisms that where each element of the array switches at a different level of acceleration.
U.S. Patent 7,554,342
For licensing information, contact the BYU Office of Technology Transfer.
Anderson, J.K., Howell, L.L., Wittwer, J.W., and McLain, T.W., "Piezoresistive Sensing of Bistable Micro Mechanism State," Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 943-950, 2006.
Anderson, Jeffrey, Piezoresistive Sensing of Bistable Micro Mechanism State," M.S. Thesis, December 2005.